Describe Keynesian Economics as It Pertains to Gdp
Salais in International Encyclopedia of the Social Behavioral Sciences 2001. What does Keynes say about Investment and interest rates Depletion accumulation.
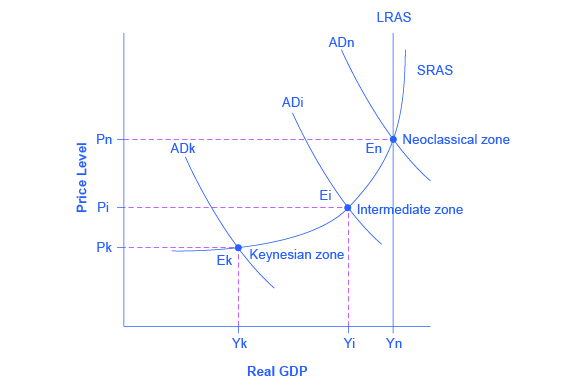
Keynes Law And Say S Law In The Ad As Model Article Khan Academy
The IS curve represents all combinations of interest rates and GDP where total spending equals total output or GDP.

. But because aggregate demand is volatile it can easily fall. Explore economic output the differences between the two models and how the models describe the economy at two. Firms produce output only if they expect it to sell.
And positions the government as a counterweight to control the magnitudes of. Keynesian economics body of ideas set forth by John Maynard Keynes in his General Theory of Employment Interest and Money 193536 and other works intended to provide a theoretical basis for government full-employment policies. This cycle can be seen as fluctuations between positive and negative GDP gaps.
This theory is named after a UK-based economist John Maynard Keynes who. The Keynesian model of effective demand consists essentially of three spending streams. Therefore increasing government expenditure and reducing taxes may increase demand in the market and pull the economy out of depression.
Keynes used his incomeexpenditure model to argue that the economys equilibrium level of output or real GDP may not corresPond to the natural level of real GDP. Simply put the difference between these theories is that. John Maynard Keynes developed this theory after the _____ _____.
Keynes is absolutely essential for an understanding of Keynesian economics. The idea is simple. Aggregate demand private consumption expenditure government expenditure investment net exports.
It stresses the fine-tuning of short-term fluctuations by. Keynesianism and State Interventionism. Private sector decisions can sometimes lead to adverse macroeconomic outcomes such as reduction in consumer spending during a recession.
Keyness theory of the determination of equilibrium real GDP employment and prices focuses on the relationship between aggregate income and expenditure. It is defined by the view that the principle of effective demand as. Real GDP depends on how much demand exists across the economy.
Keynesian economics is the view that in the short run especially during recessions economic output is strongly influenced by aggregate demand total spending in the economy. Consumption expenditures investment expenditures and government expenditures each of which is independently determined. The Keynesian perspective focuses on aggregate demand.
The Keynesian view of the world was articulated by Sir John Hicks in the IS-LM model which became the macroeconomic model used by policy makers for the next few decades. The LM curve represents equilibria in the money market. A prior knowledge of the fundamental ideas of JM.
The basic and fundamental ideas on which Keynes theory of employment has been built areeffective demand consumption function investment saving marginal efficiency of capital multiplier liquidity preference. In the incomeexpenditure model the equilibrium level of real GDP. Keynesian Economic Theory is an economic school of thought that broadly states that government intervention is needed to help economies emerge out of recession.
There are three principal tenets in the Keynesian description of how the economy works. Describe Keynesian Economics as it pertains to GDP Be sure to include. Spending and tax cuts help an economy by raising demand.
In the Keynesian view aggregate demand. Consumption investment government purchases and net exports. Keynesianism assigns to the State the responsibility to regularly intervene in the operation of the economy so as to maintain its performance at a high level.
An economys output of goods and services is the sum of four components. Keynesian economists argue that since the level of economic activity depends on aggregate demand but that aggregate demand cant be counted on to stay at potential real GDP the economy is likely to be characterized by recessions and inflationary booms. Aggregate demand is influenced by many economic decisionspublic and private.
Central to Keynesian economics is an analysis of the determinants of effective demand. Economics questions and answers. Thus while the availability of the factors of production determines a nations potential GDP the amount of goods and services actually being produced and sold ie.
Keynesian economics explains GDP which is a measure of national output as determined by employment which is turn is determined by aggregate demand and aggregate supply. His ultimate goal was to tell. The idea comes from the boom-and-bust economic cycles that can be expected from free-market economies.
What does Keynes say about consumption and savingsdis-savings What does Keynes say about Investment and interest rates Depletion accumulation What does Keynes say about Government. Keynesian economics focuses on the role of aggregate spending in determining the level of real GDP. Keynes argued that for reasons well explain shortly aggregate demand is not stableit can change unexpectedly.
The Keynesian Model and the Classical Model are used to describe economic growth. Keynesian economics dominated economic theory and policy after World War II until the 1970s when many advanced economies suffered both inflation and slow growth a condition dubbed stagflation Keynesian the-orys popularity waned then because it had no appropri-ate policy response for stagflation. Monetarist economics referst to Milton Friedman s direct criticism of the Keynesian economics theory formulated by John Maynard Keynes.
Keynesian economics is a theory that relates total spending with inflation and output in an economy. Keynesian economics ˈkeɪnziən KAYN-zee-ən. View Answer Explain a major strength and a major weakness of.
It was the dominant school of macroeconomics and represented the prevailing approach to economic policy among most Western. Keynes Describe Keynesian Economics as it pertains to GDP Be sure to include What does Keynes say about consumption and savingsdis-savings. A form of demand-side economics that encourages government action to increase and decrease demand and output.
What does Keynes say. Post-Keynesian economics PKE is an economic paradigm that stems from the work of economists such as John Maynard Keynes 1883-1946 Michal Kalecki 1899-1970 Roy Harrod 1900-1978 Joan Robinson 1903-1983 Nicholas Kaldor 1908-1986 and many others. Foreign trade is ignored.
Because is potential output the economy is at full employment. The idea that govt. Sometimes Keynesianism named after British economist John Maynard Keynes are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand total spending in the economy strongly influences economic output and inflation.
Suppose the economy starts where intersects at and in the diagram above.
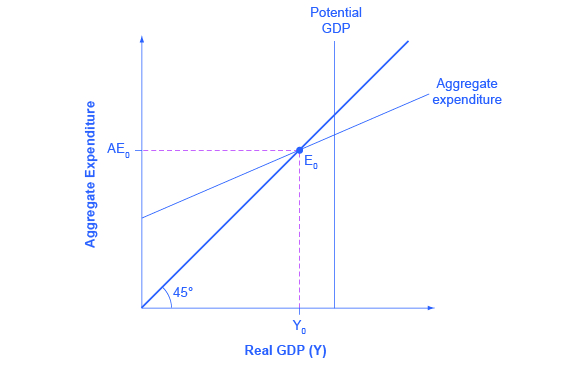
The Expenditure Output Or Keynesian Cross Model Article Khan Academy

Keynesian Economic Policy Macroeconomics

Keynesian Economic Policy Macroeconomics
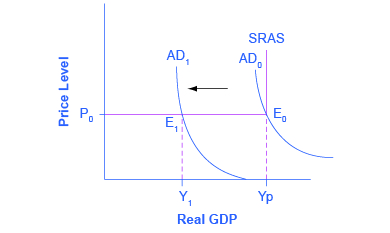
The Building Blocks Of Keynesian Analysis Article Khan Academy
No comments for "Describe Keynesian Economics as It Pertains to Gdp"
Post a Comment